Revit Architecture
 Overview:
Overview:
Revit Architecture a Building Information Modeling (BIM) software tool introduced by Autodesk. This software is specially designed for architects, structural engineers, engineers, and contractors.
It is mainly used for creating optimized & accurate designs from concepts to visualization. It helps to capture & analyze design concepts followed by maintaining coordinated design data accurately through documentation and construction. It permits designers to design a structure and its components in 3D then annotate the model with 2D drafting elements followed by accessing the structure information from the building models database.
Revit software is set of tools which is useful for various phases of building construction lifecycle i.e. from concept to construction and later destruction.
 Why to learn?
Why to learn?
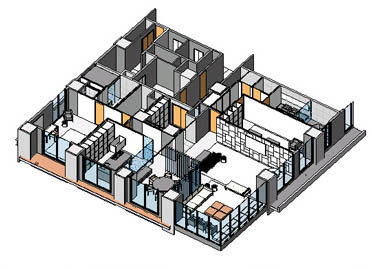
Revit software brings tools to support architectural designers, MEP engineers, structural engineers, and constructors. Revit is specially designed for BIM (Building Information Modeling) to design, build, and maintain higher-quality, and energy-efficient building designs. Complete features make this tool an ideal solution for the whole building project team.
By learning Revit, one as a design and construction expert, will be able to make ideas from concept to construction with a synchronized and steady model-based approach.
 Learning Objectives:
Learning Objectives:
CADD Center will help you to ace the associated features of Revit Architecture:
- Analysis: Element energy analysis of the Building; Improved structural analytical model; Duct & pipe estimations to API; Physical materials for performance analysis
- Collaboration: Work-sharing – several users save their work to a central file; collaboration on shared models across a Wide Area Network (WAN); work from remote locations using a local server.
- Design: More simple to model, edit, and document designs of stairs & railings; parametric components - graphical system for design, shape making; HVAC/electrical design room color-fill plans and communication of design intent, visually.
- Visualization for designing displaced building design views; enhancement of performance for visualization; capturing of drawing ideas in a photorealistic state, and reduction of project charge with cloud-based rendering.
 Learning Outcome:
Learning Outcome:
- Student will learn to develop higher-quality, more accurate architectural designs; use tools specifically built to support Building Information Modeling workflows.
- Students will learn to capture and analyze concepts, and maintain your vision through design, documentation, and construction.
- Students will learn to do building element energy analysis; use the API to perform pipe/duct calculations; perform static analysis from the cloud; create/manage the structural analytical model; automatically update your model with analysis results; and improve BIM-based building performance workflows.
- Student will learn to scan Revit model for collisions between elements; work with multiple users and save their work to a central file; collaborate on shared models across a WAN; streamline data management; and work from remote locations using a local server.
- Student will learn to dock dialogs in a single window; more easily model, edit, and document designs; place air terminal devices on duct faces; restrict angles for pipe, duct, and cable tray; cap open ends of pipe or duct content quickly; rebar placement constraints customization; gain control over rebar placement; and get more rebar options when modeling.
- Student will learn to crop non-rectangular model areas faster; easily manage elevation cut-line configuration; automatically display dimension values; annotate multiple elements with a single tag; define geometry and position for beams and braces; get greater control of schedule formatting; derive construction insight from design models; calculate/track detailed material quantities, display totals in current or load values, and create details from views of a 3D model.
 Overview:
Overview: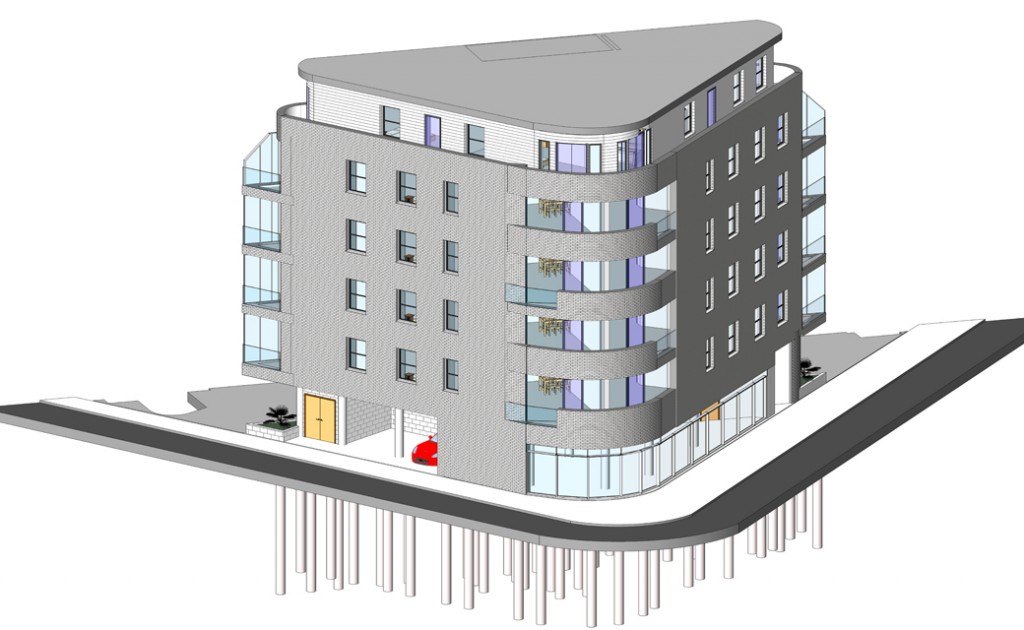
 Why to learn?
Why to learn? Learning Objectives:
Learning Objectives: Learning Outcome:
Learning Outcome: